When seconds count, CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) can mean the difference between life and death. It’s a critical skill that restores blood flow and oxygen to the vital organs, offering a lifeline in emergencies like cardiac arrest or respiratory failure. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or a concerned bystander, understanding CPR is essential to saving lives.
This guide dives into everything you need to know about CPR, including its process, history, role in healthcare, and the importance of proper training. By the end, you’ll understand not just its importance but also how to take action that could save someone’s life.
What Is CPR and Its Role in Healthcare
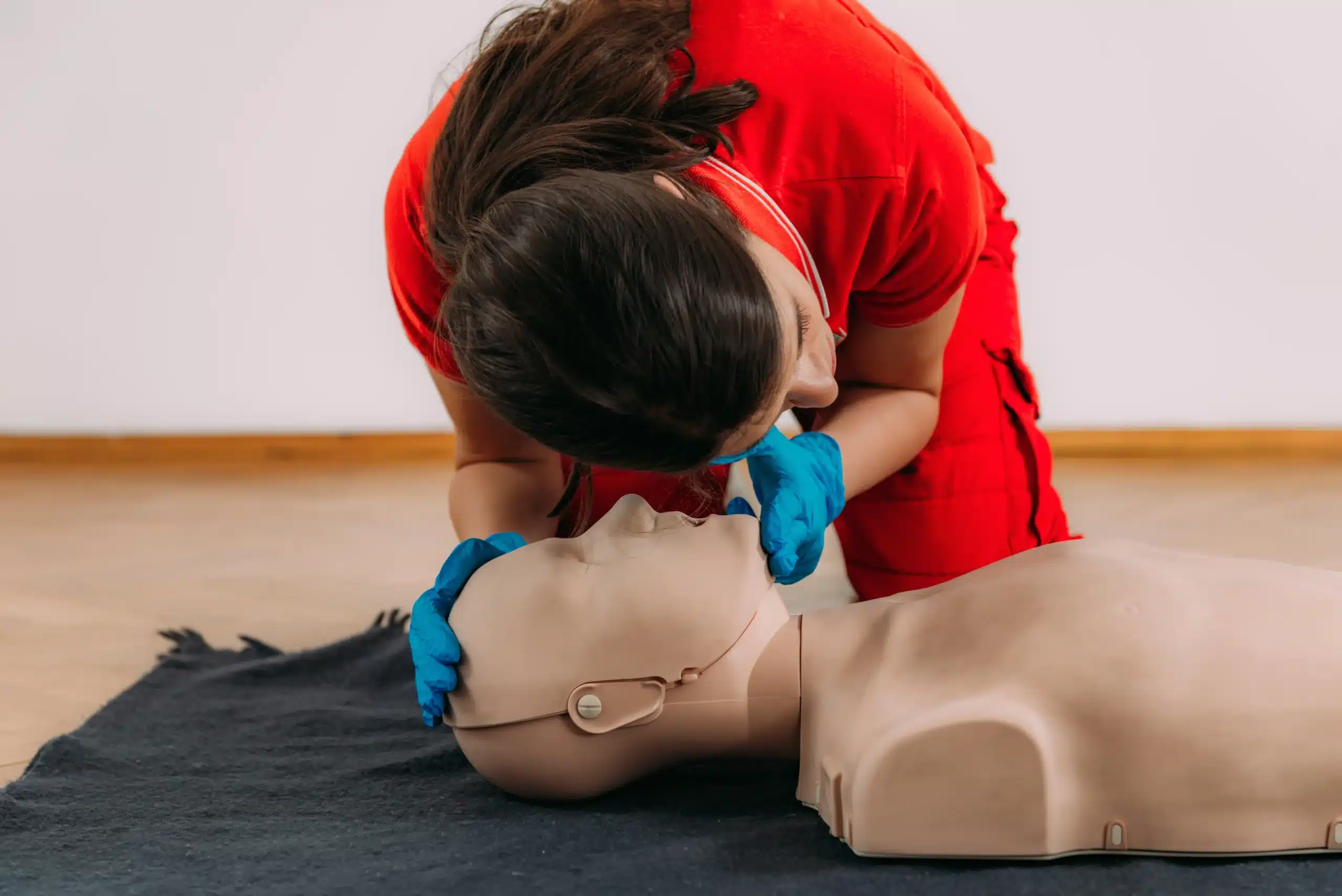
CPR, or Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, is a life-saving technique used in cardiac emergencies like heart attacks or drowning when someone’s breathing or heartbeat has stopped.
The Process of CPR
CPR involves two key steps:
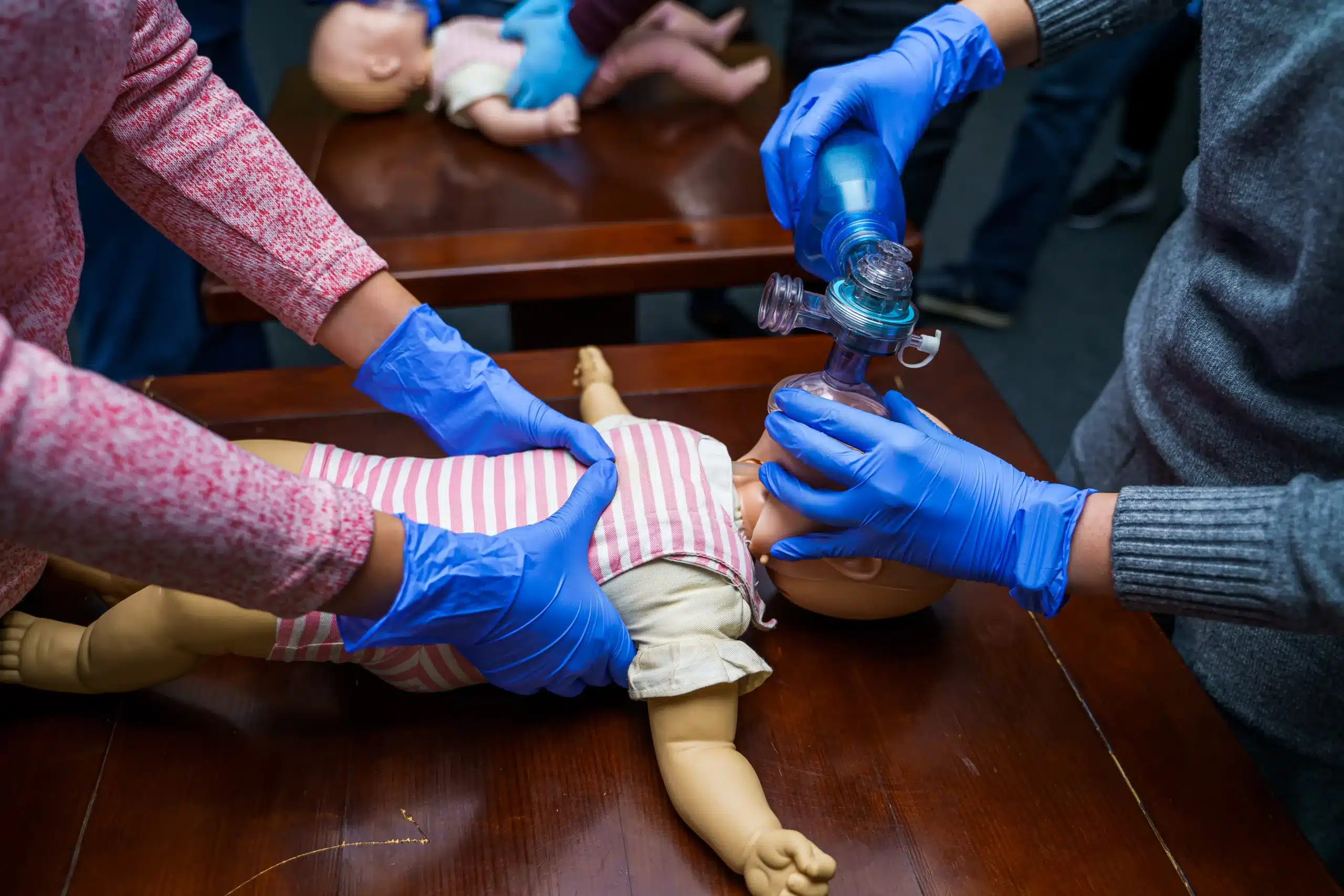
- Manual Chest Compressions – Compressions help maintain circulation, pushing blood to the brain and vital organs.
- Rescue Breaths – Breaths supply oxygen to the lungs, ensuring oxygenation when spontaneous breathing ceases.
Its primary purpose is to delay damage to vital organs while professional medical help is on the way. By keeping the heart and brain functional, CPR serves as a bridge to advanced care, such as defibrillation or emergency room treatment.
Universality of CPR
CPR isn’t just for healthcare professionals; anyone can learn how to perform it. From hospitals to public emergencies—on the street, at home, or in offices—CPR is universally applicable. Whether you’re a nurse or a passerby, timely action is critical in saving lives.
A Brief History of CPR
CPR has come a long way since its early days. Here’s a quick look at its evolution:
- 1950s – Mouth-to-mouth resuscitation was introduced.
- 1960s – The American Heart Association (AHA) embraced CPR and began formal training programs.
- Today – Modern techniques are evidence-based, focusing on high-quality chest compressions and updated protocols reflecting the latest scientific research.
These milestones emphasize CPR’s continued improvement to become the life-saving technique it is today.
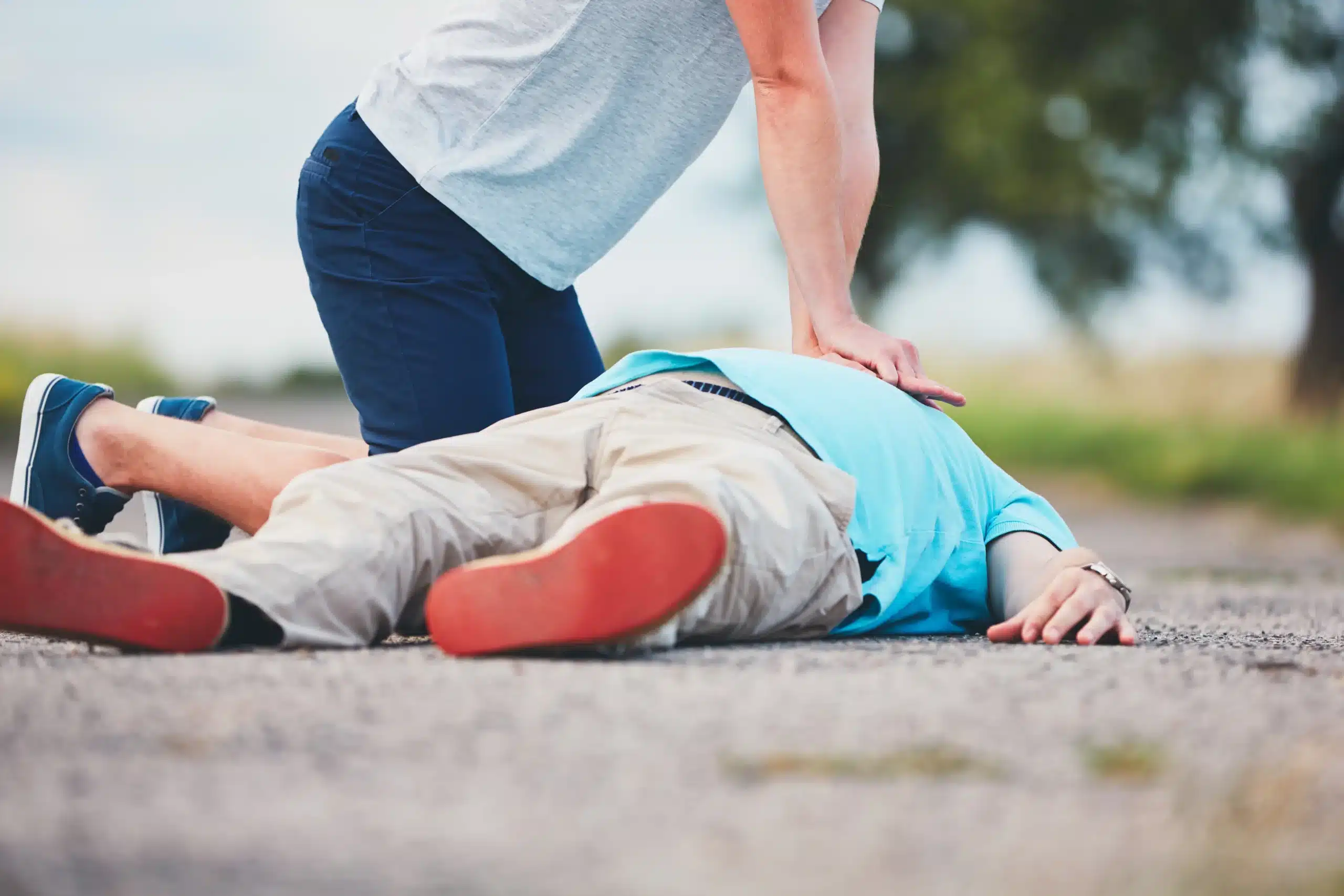
Importance of CPR in Saving Lives
Every year, hundreds of thousands of cardiac arrests occur outside hospitals. Immediate CPR can double or even triple their chances of survival.
The Chain of Survival
The “chain of survival” illustrates the critical steps to improving outcomes in cardiac emergencies:
- Immediate recognition of cardiac arrest.
- Early CPR with high-quality chest compressions.
- Rapid defibrillation.
- Advanced life support.
CPR is the most important link in this chain, providing critical time until professional help arrives.
Bystander CPR’s Impact
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrests often occur in homes or public spaces. Despite its simplicity, many potential rescuers hesitate to intervene. Studies show that bystander CPR can increase survival rates by as much as 300%—a life-altering difference.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals in CPR
Healthcare professionals are the first line of defense in many emergencies. Their ability to perform swift and effective CPR is often critical to the patient’s survival.
Why Competency Matters
Healthcare workers are expected to master CPR as part of their training. Regular practice ensures that critical steps can be performed under pressure without hesitation.
Roles such as nurses, paramedics, and even hospital administrators must stay updated on techniques to deliver high-quality care. Lives often depend on their quick thinking and skill.
Ongoing Training is Key
CPR techniques evolve. Advances in research often prompt changes to protocols. For healthcare professionals, ongoing certifications ensure they are always up to date.
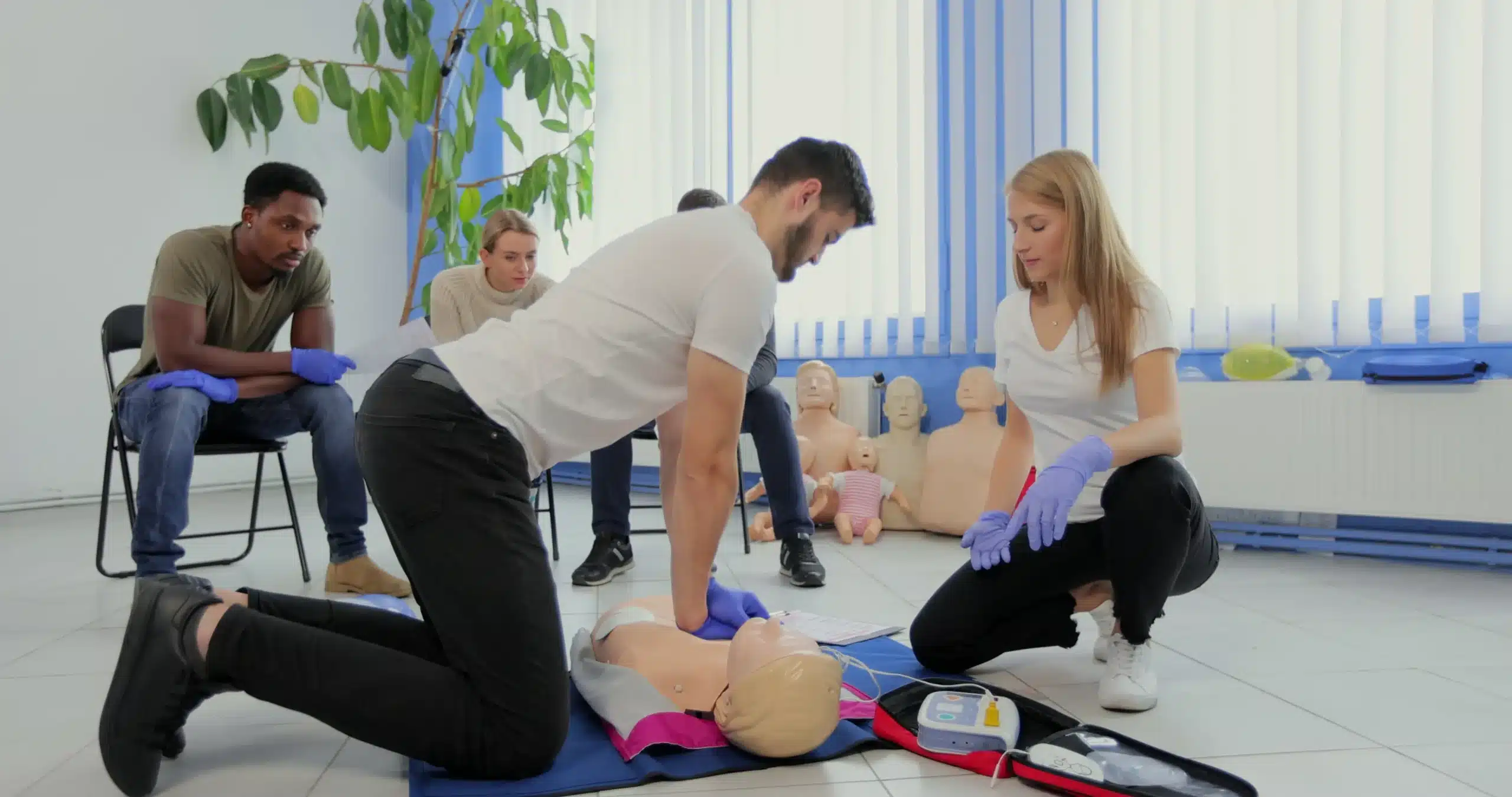
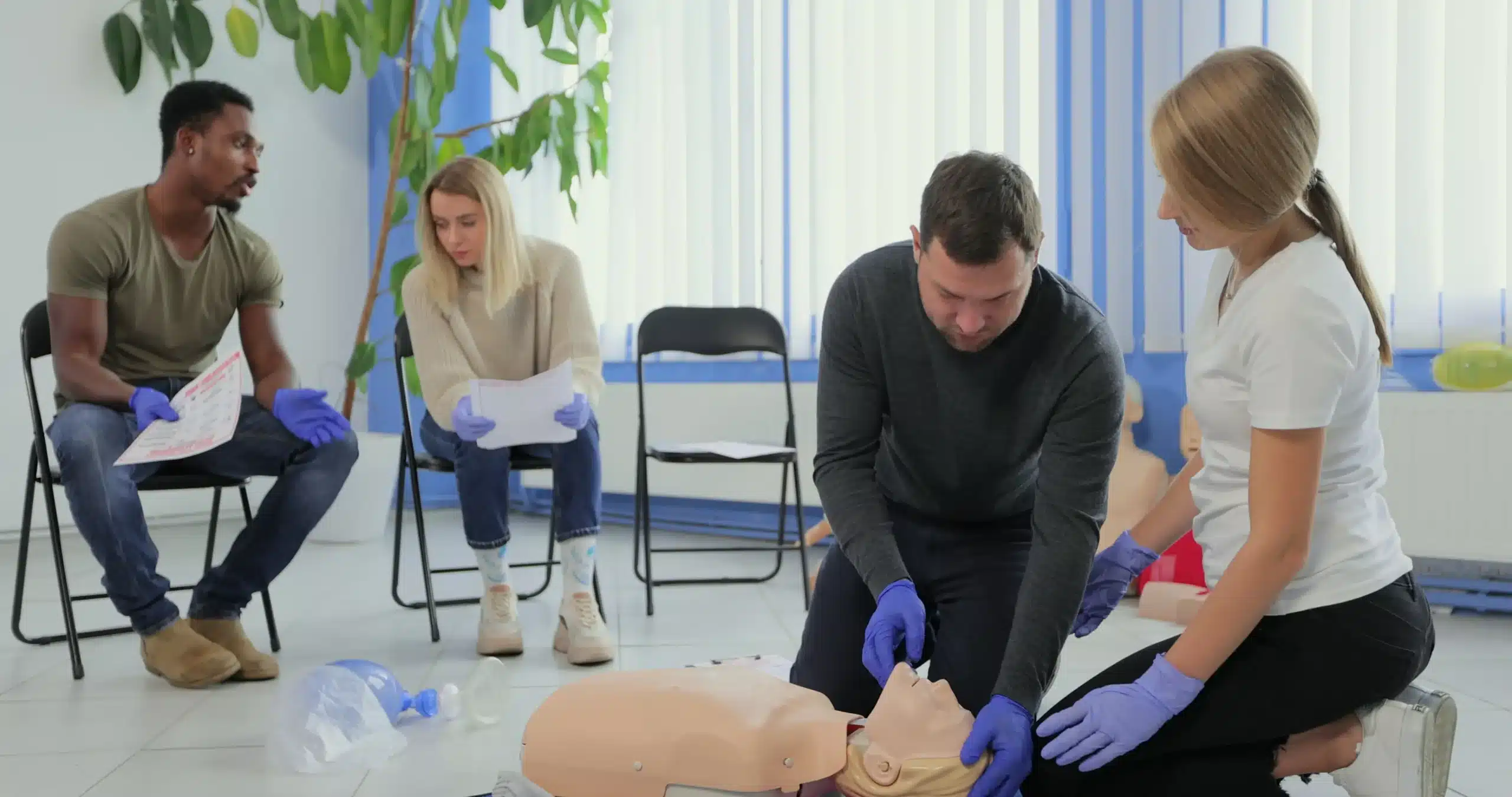
CPR Training and Certification
Proper training equips people with the skills and confidence to act in emergencies.
How to Become CPR Certified
- Find a Training Center: Organizations like Safety Training Seminars offer AHA-certified CPR courses in multiple formats.
- Complete the Training: Basic CPR training typically takes only a few hours and covers both theory and practical skills.
- Earn Certification: Successfully completing the course awards a certification that remains valid for up to two years.
Levels of Certification
- BLS (Basic Life Support): For healthcare providers focusing on chest compressions, airway management, and defibrillation.
- ACLS (Advanced Cardiac Life Support): For advanced healthcare settings, emphasizing team-based interventions.
- CPR and First Aid: For general use, aimed at non-healthcare professionals.
Even non-professionals can dramatically impact survival rates by becoming CPR-certified.
Debunking Myths About CPR
Unfortunately, misconceptions about CPR prevent many from stepping in during emergencies. Let’s clear up a few myths:
- Myth #1: “Only trained professionals should perform CPR.”
Fact: Even imperfect CPR can be lifesaving. The decision to act is far more important than hesitating.
- Myth #2: “CPR always brings someone back to life.”
Fact: CPR doesn’t always restart the heart—it buys time until advanced care arrives.
- Myth #3: “Doing CPR might hurt the person.”
Fact: While chest compressions are forceful, the risk of harm is minimal compared to the consequences of inaction.
Building a Safer Community Through CPR
When more people are trained, communities become safer places. Accessible CPR training ensures a widespread ability to respond to emergencies, increasing survival rates nationwide.
CPR is not just vital for healthcare professionals—it’s an essential skill that everyone should have.
Key Takeaways
- Role of CPR: A life-saving technique for maintaining circulation and oxygenation during cardiac emergencies.
- Importance for Healthcare Workers: CPR competency is non-negotiable for medical professionals.
- Training Options: Safety Training Seminars offer AHA-certified courses like CPR and First Aid, BLS, ACLS, and PALS.
Take Action Today
Are you ready to become a hero in someone’s life? Get CPR-certified with Safety Training Seminars. Explore our range of courses, from CPR and First Aid to BLS and ACLS, and ensure you’re equipped with the skills that save lives.